Synthetic Metric Scale Survey Likelihood to Purchase the Product Again
Eric Risen and Larry Risen, BioTrak Inquiry Inc.
December 19, 2008 ~ Market researchers usually use a mathematical technique called intent calibration translations to catechumen a respondent'due south stated purchase intentions into bodily purchase probabilities. Intent scale translations provide the researcher with an estimate of actual ownership behavior and accounts for over interpretation on the part of respondents' participation in the research. Companies can then rely on purchase intentions to forecast the purchase of new products or repeat purchase of existing products. In other words, if a client states that he/she prefers a particular product over another, what is the probability that he will actually follow through with making the purchase of the preferred product?
Studies have shown that consumer's self-reported intentions to purchase exercise not reliably predict their purchasing behavior (one). Market place researchers needed to develop a method to more than accurately translate a respondent's response to survey questions into actual probabilities that they would buy or use a product of interest. Intent scale translations take information from a customer survey on purchase intentions and convert the data into a prediction of purchase probability by using comparisons of stated vs. bodily purchase behavior.
Traditional intention rating scales use a 5-signal scale to bear witness consumer's intentions of buying a product. In this traditional method, people who scored a rating of one or ii were typically assigned a 0% adventure of ownership the product. The enquiry of Thomas Juster (2)found that the v-point scale was an inaccurate style of measuring heir-apparent intention and that a buyer with a score of 1 and 2 actually had a greater than 0% risk of buying the production. Juster created his ain heir-apparent intention scale that would ameliorate a marketer'southward power to forecast behavior from intentions and business relationship for changes in a consumer's truthful intentions between the time surveyed and the time of actual buy. Juster developed an intention scale that adjusted the intention scores by analyzing the actual futurity purchase behavior of consumers later being surveyed. He adult a new eleven-point calibration which implied simple methods for computing intentions. It stated that if a sample grouping was asked if they would purchase a new car in the next month and they were to choose a number correlating to the likelihood on a calibration of 0 to ten, x being the greatest possibility, and the average score came out to exist 2.five out of 10 then that would translate to 25% of the general population purchasing a new car in the next year. The research described hither will provide a demonstration of how buy intention scales are used to predict bodily consumer purchase behavior.
The traditional 5-point calibration is used to give a general estimate on consumer's purchase intentions of something. It tin be used to predict everything from consumer's intention on buying a certain product to predicting where people may travel for vacation or fifty-fifty the likelihood of a doctor ordering a particular diagnostic test for a patient. The v point calibration is routinely used across many types of businesses and industries. Beneath is a typical scale and description of a v betoken Intention Calibration.
Tabular array ane. Example of 5-Point Intention Scale

The v-betoken calibration, as well referred to as the Likert scale, is yet commonly used past major corporations to sympathize consumer'due south product purchasing intentions or but conducting basic surveys. It is particularly useful in telephone surveys and mall inquiry where consumers are taking a verbal survey and their responses are existence recorded by the researcher.
One major corporation that nevertheless uses this 5-signal scale is Air conditioning Nielsen, a marketing research company that conducts surveys on a variety of consumer products. Air-conditioning Nielsen provides a service called BASES to present pre-market insights to consumer goods companies. Consumer good manufacturers often use outside market researchers for conducting unbiased surveys. BASES has become the industry standard forecasting model. Table 2 demonstrates how a 5-point scale is translated into buy probability. Annotation that Intent Probability overestimates predicted probability when comparing to the AC Nielsen BASES translation scale (3). AC Nielsen and others take conducted diary studies where consumers record their actions for the researcher over time and follow-upwardly market research to measure actual observed purchase behavior compared to stated intentions. This has resulted in establishing a correction cistron that adjusts the intent probabilities of purchase.
Tabular array ii Apply of 5-Indicate Intention Calibration in Translating Purchase Probability

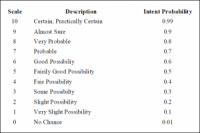
As previously mentioned, some other mutual buy intention scale used is the xi-point scale, created by Thomas Juster, which he found to be much more accurate than the 5-betoken calibration. On the Juster scale, every clarification correlates straight to a number ranking of 0 to ten. The reason for this alternative scale is to requite college values to people ranking lower scores. In the 5-indicate calibration, someone who receives a score of 1or 2 were sometimes assigned a 0% risk of using the product. Juster institute this to be incorrect and fix out to fix it by coming up with his own calibration. In the 11-point scale in Table 3, the score relates direct to the probability of employ. For example, someone with a score of 4 is constitute to accept a twoscore% risk of using the product.
Table iii. Juster'southward 11-Betoken Probability Scale
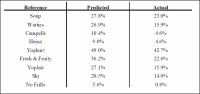
Herein we report a review of consumer studies as it relates to a Translated Probability Intent Scale. What I found was a research written report on Fast-Moving Consumer Goods. This particular report observed iii popular types of soups and four types of yogurt. It involved a face-to-face survey performed by the Palmerston North Household Double-decker survey (4). The consumers were asked nearly their purchase intent of each of the items and an overall percentage of buy probability was obtained. Then the respondents were re-interviewed by telephone a month after the original survey and estimates of actual purchase intent were obtained. For example, Fresh and Fruity yogurt had a predicted purchase rate of 36.2%, only when the respondents were re-contacted, only 22.6% had really purchased the Fresh & Fruity yogurt. This indicates an overestimation of expected purchase intent by13.6%. Tabular array 4 shows the results from this survey for various products.
Table 4. Purchase Intention Using Juster's 11-betoken Scale
Nosotros plotted all of the actual and predicted probabilities on a scatter plot with Predicted Purchase Intent on the X-axis and Actual Buy Behavior on the Y-axis. In Figure one the graph and equations generated from the 11-point Juster scale results are shown.
Figure 1. Juster 11-Bespeak Scale: Predicted vs. Actual
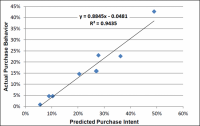
Each mark represents a unique study. A "best fit" regression line was applied to the resulting plot using the best fit line feature in Excel and the equation of the line was calculated. The regression line shows y = 0.8845x – 0.0481. The linear correlation coefficient, r, gave a stiff correlation coefficient of r = 0.9713. A perfect correlation is + i where all points lie on a directly line. A correlation coefficient greater than 0.eight is considered strong (Marino 149). The coefficient of determination, R2, was calculated and found to be R2 = 0.9435.
Nosotros took the Juster Scale Intent Probability numbers in Table three and entered into them into the regression equation, y = 0.8845x – 0.0481 (ten= 0.99, 0.9, 0.8, etc). These represent the predicted purchase probabilities "x" in the equation. The decimals are then converted dorsum into percentages for the concluding Translated Probability Table 5 below:
Table 5. Simply Scale Translated Probabilities
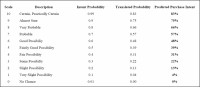
From this analysis 83% of actual intended buyers (those with a scale score = 10 described as certain purchasers) tin can exist expected to buy the product vs. number predicted. Of those with a score of nine and intent probability of 90%, only 75% would actually be predicted to buy the product. Of those with a score of 5 and intent probability of 50%, just 39% would actually be predicted to purchase the product. This demonstrates how statistics can exist used in intention scale translations to better predict a consumer's actual purchase intent from survey data. Statistics like this are used by market place researchers to help guide marketing, advertising and sales forecasts for product manufacturers.
To download a PDF version, click here.
Bibliography
i. Sheppard, Blair H., Jon Hartwick, and Paul R. Warshaw. "The Theory of Reasoned Action: A Meta-analysis of Past Inquiry with Recommendations for Modifications and Future Research." Journal of Consumer Research 15.iii (1988); 325-343.
2. Juster, F. Thomas. "Consumer Buying Intentions and Buy Probability: An Experiment in Survey Pattern." Journal of the American Statistical Clan 61 (1966); 658-696.
3. Chandon, Pierre, Vicki M. Morwitz, and Werner J. Reinartz. "Do Intentions Really Predict Behavior? Self-Generated Validity Effects in Survey Research." Periodical of Marketing 69 (2005); 1-14.
iv. Brennan, Mike, and Don Esslemont "The Accurateness of the Juster Scale for Predicting Buy Rates of Branded, Fast-Moving Consumer Goods." Marketing Bulletin 5 (1994) : 47-52
v. Marino, Kenneth East., Forecasting Sales and Planning Profits. Chicago: Probus Publishing, 1986.
six. The Nielsen Company. Marketing Intelligence. xiii Dec. 2008 <http://www2.acnielsen.com/site/alphabetize.shtml>.
Source: https://biotrak.com/hello-world/
Post a Comment for "Synthetic Metric Scale Survey Likelihood to Purchase the Product Again"